Nature and Rate of Change
|
Climate change
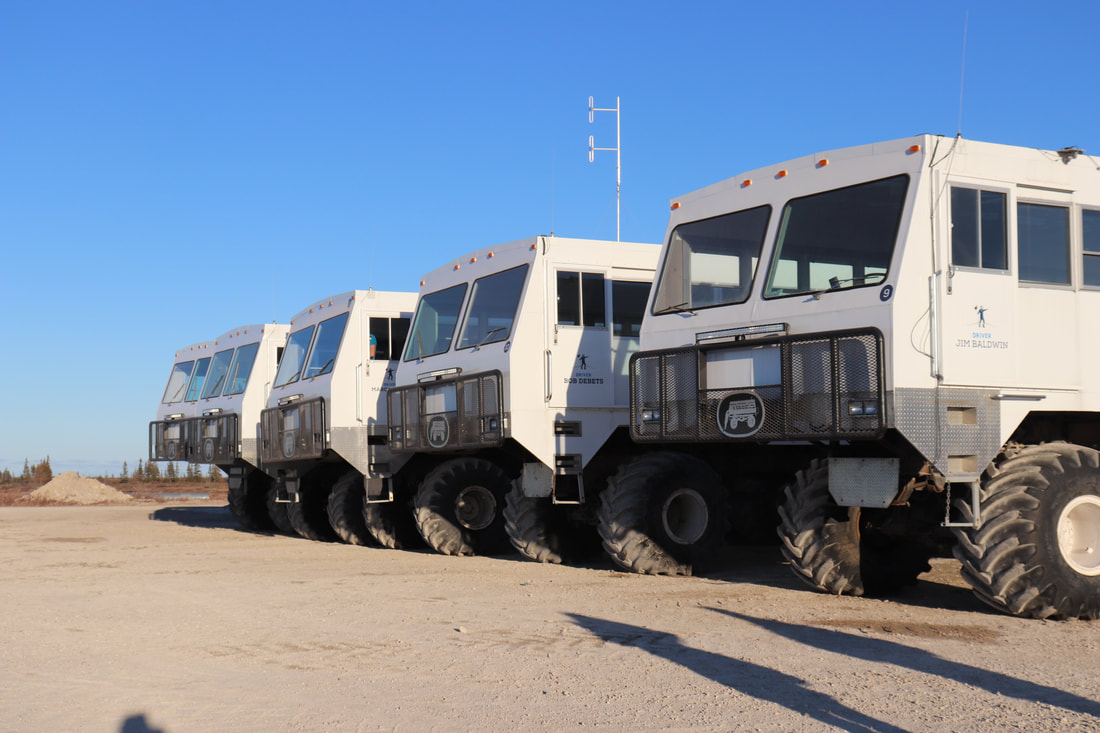
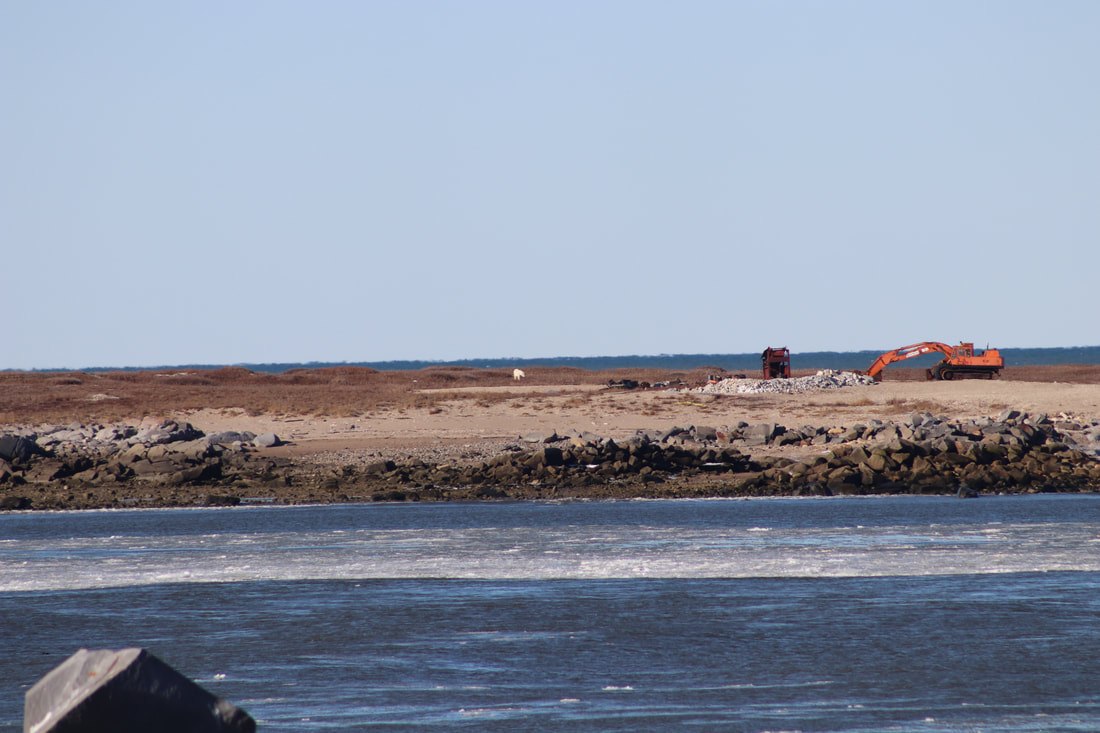
Climate change is resulting in a milder, shorter winter season and longer, warmer summers. Average yearly arctic temperatures are increasing. The shrubs are growing taller on the tundra and the surface temperature of water in Hudson Bay has increased by 3 degrees in the past 20 years. Climate change is likely to change migratory patterns, population numbers and physical characteristics of species. The reduction in the thickness of sea ice, is making it difficult for polar bears to hunt for their primary dietary staple seals. In turn, this is changing polar bear feeding patterns, migration paths and many are experiencing a reduction in body weight. Bears are staying on shore longer to wait for the ice to form. Migratory birds are changing their movement patterns. Click to read As polar bears wait, let's talk about ice. Thawing permafrost Increased temperatures are resulting in sea ice melts and reduced ice cover on Hudson Bay. Permafrost melts are likely to result in increased decomposition and microbiotic activity and release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Tourism Tourism in and around Churchill focuses on polar bears, beluga whales, nature photography and the Aurora Borealis. While activities are intended to minimise human impacts on wildlife, the actions of individuals are difficult to predict and control. Some passengers, in trying to attract the attention of bears for better photographs may bang on the side of the tundra buggy, hiss or whistle to encourage the bear to move. Bears are exposed to the tundra vehicles from around 9am to 3pm each day. In periods where there are low polar bear numbers, multiple vehicles will crowd around the one bear or family of bears. In attempts to ensure polar bear viewing tundra buggies may use any tracks or trails that are available rather than using the roads designed for the purpose. This could result in erosion of tracks or destruction of vegetation. |